Bitcoin halving is a pivotal event in the cryptocurrency world, one that has historically signaled significant shifts in market dynamics and investor sentiment. Occurring approximately every four years, this event reduces the reward for mining new blocks by half, thereby diminishing the rate at which new bitcoins are generated. As we delve into the annals of Bitcoin’s history, it becomes evident that each halving event has left a distinct mark on the cryptocurrency’s journey. This article, crafted for the keen readers of decentrahacks.com, aims to explore the historical context of Bitcoin halving, its implications on the market, and what past events can tell us about the future of this digital currency.
Table of Contents,
The Genesis of Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin’s underlying technology, blockchain, was designed with a deflationary mechanism to mimic the scarcity and value preservation seen in precious metals like gold. The halving events are part of this mechanism, ensuring that Bitcoin remains a scarce resource. The first halving in 2012 slashed the reward from 50 to 25 bitcoins per block, a monumental event that began the tradition of closely watching halving dates and speculating on their market impacts.
Historical Halvings and Market Reactions
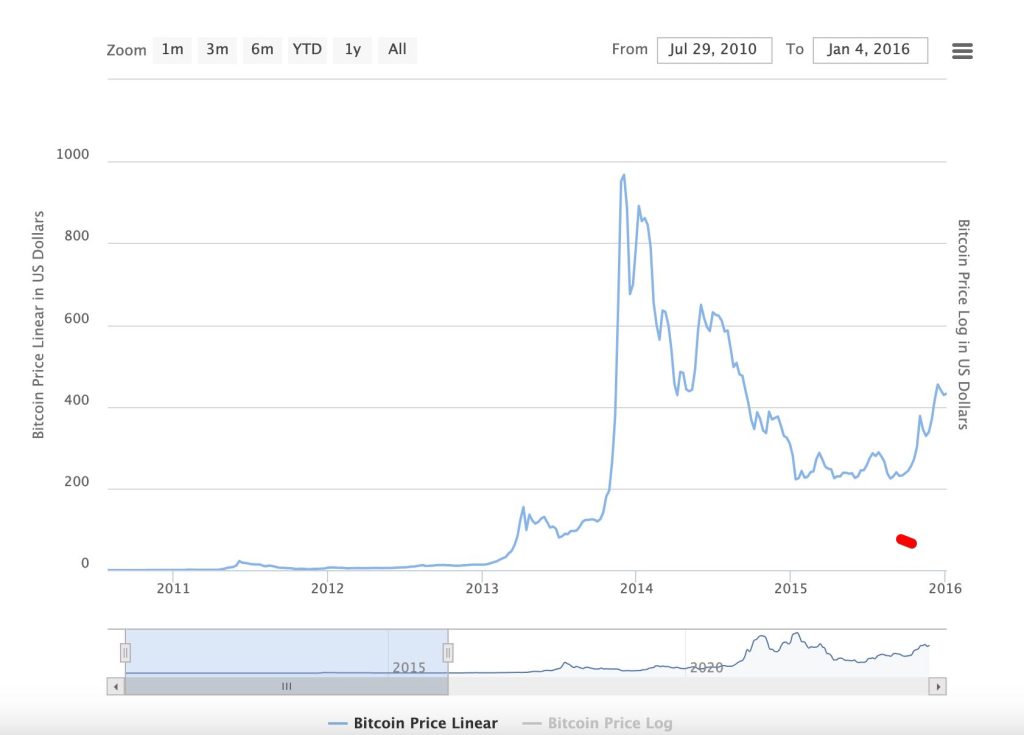
2012 Halving: The inaugural halving event saw Bitcoin’s price slowly but steadily rise, setting the stage for a bull run that would peak in late 2013. This event demonstrated the potential impact of reduced supply on price, serving as a case study for the supply-demand dynamics in the cryptocurrency market.
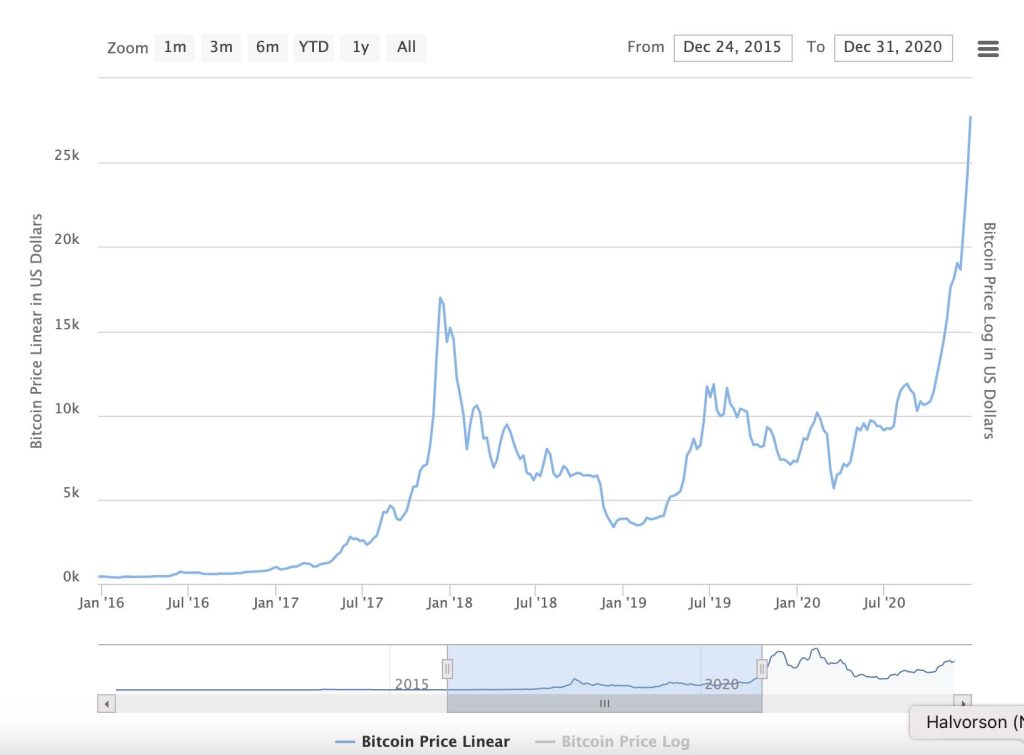
2016 Halving: The second halving reduced the reward to 12.5 bitcoins per block. Following this event, Bitcoin entered a period of volatility before embarking on an unprecedented rally in 2017, hitting all-time highs and capturing the attention of mainstream investors and the general public alike.
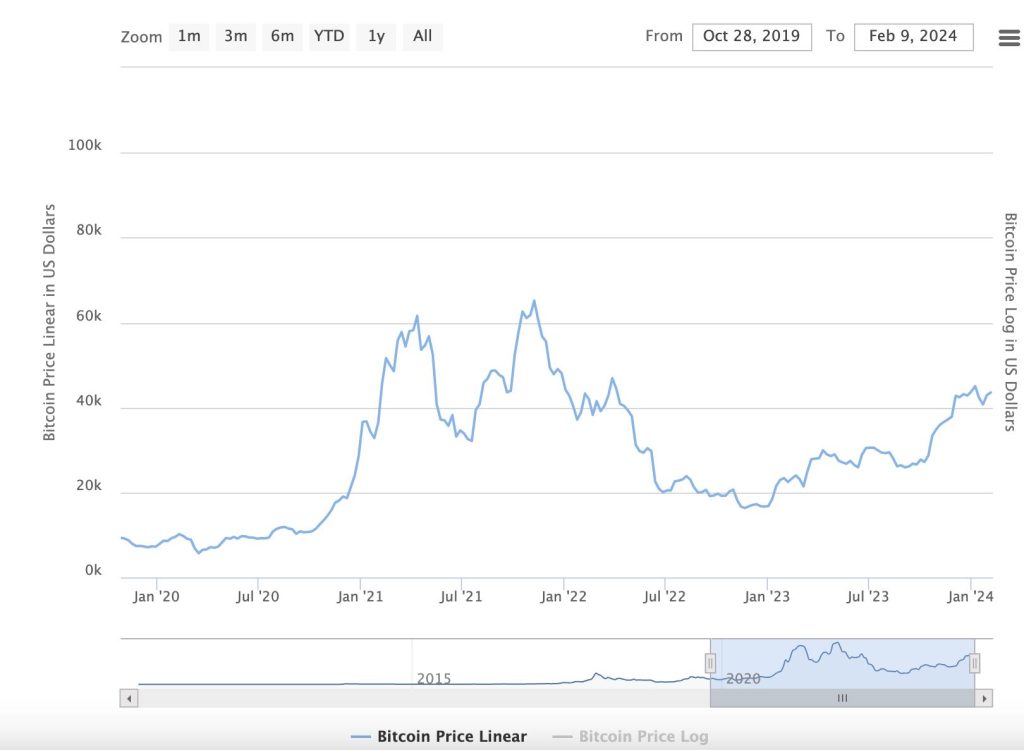
2020 Halving: The most recent halving, which reduced the block reward to 6.25 bitcoins, occurred during a tumultuous time marked by a global pandemic. Despite initial uncertainty, Bitcoin saw a significant price surge in the months following, reaching new heights in early 2021 and solidifying its position as a contender in the financial markets.
The Argument for Halving as a Bullish Catalyst
Proponents of Bitcoin halving argue that these events are inherently bullish, driven by the basic principles of supply and demand. As the rate of new Bitcoin generation decreases, assuming demand remains constant or increases, the price should theoretically rise. Additionally, halving events draw increased media attention to Bitcoin, potentially attracting new investors and further driving up demand.
The Counterargument: Predictability and Market Efficiency
Critics, however, suggest that because halving events are predictable, their effects are already priced into the market by the time they occur. This perspective argues that the efficient market hypothesis applies to Bitcoin as much as it does to traditional financial markets, meaning that all known information (including upcoming halvings) is already reflected in the current price. They contend that any significant price movements associated with halvings are more likely the result of broader market trends or external factors rather than the halving events themselves.
Conclusion
The history of Bitcoin halving presents a fascinating study of how programmed scarcity can influence a digital asset’s market dynamics. While there is a compelling argument to be made about halvings serving as a bullish catalyst for Bitcoin, the predictability of these events and the efficiency of the market introduce a level of complexity to this narrative. As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature, the impact of future halvings may evolve, influenced by a growing investor base, regulatory changes, and the ever-changing landscape of digital finance. Regardless of one’s stance on the matter, halving events undeniably represent significant milestones in Bitcoin’s history, offering valuable insights into the interplay between scarcity, demand, and market psychology.



